How To Create Successful SEO Marketing Strategies For Your Small Business

If you’ve done any research at all about SEO marketing strategies, you know there’s an abundance of information out there. It can be quite confusing about where to start, what to prioritize, not to mention what really makes sense for your business.
In my opinion, you need three different SEO marketing strategies to effectively optimize your website for the search engines. In a nutshell you need:
- A strategy for the website itself
- Another for each of the pages on your website
- And one for other sites
But that doesn’t mean you need to do them all at once. You just need to plan and tackle the three strategies starting with the website itself.
SEO Marketing Strategy For Your Website
Let’s start with the SEO strategy for your website. The basic idea here is to make sure the search engines consider your site user-friendly.
Google works hard to make sure that when you search for something that the results it returns are exactly what you want – not only from a content perspective, but from an ease-of-use perspective. So, Google wants websites to be fast, error-free, easy to navigate, secure and, of course, mobile friendly.
(We’ll visit the issue of great content when we talk about the SEO marketing strategy you need for each of the pages on your website.)
Have you ever visited a website that seemed to take FOREVER to load? Did you get frustrated that the information or entertainment you wanted access to wasn’t immediately available? I know my patience is tested when what I want to view doesn’t immediately appear when I ask for it. And I’ll bet your reaction isn’t too different from mine.
Sometimes the long loading times are the result of how hard your computer is working. Other times the delayed response is due to your internet connection. And sometimes it’s due to the speed of the website you’re visiting.
Obviously, you don’t want your customers visiting your website only to feel frustrated by how long it takes for your website to load. But you can only do so much about it.
You can’t do anything about how hard your customer’s computer is working or their internet connection, but you can do something about the speed of your website.
The quickest way to begin getting a handle on your website’s speed is to use a free Google tool called PageSpeed Insights.
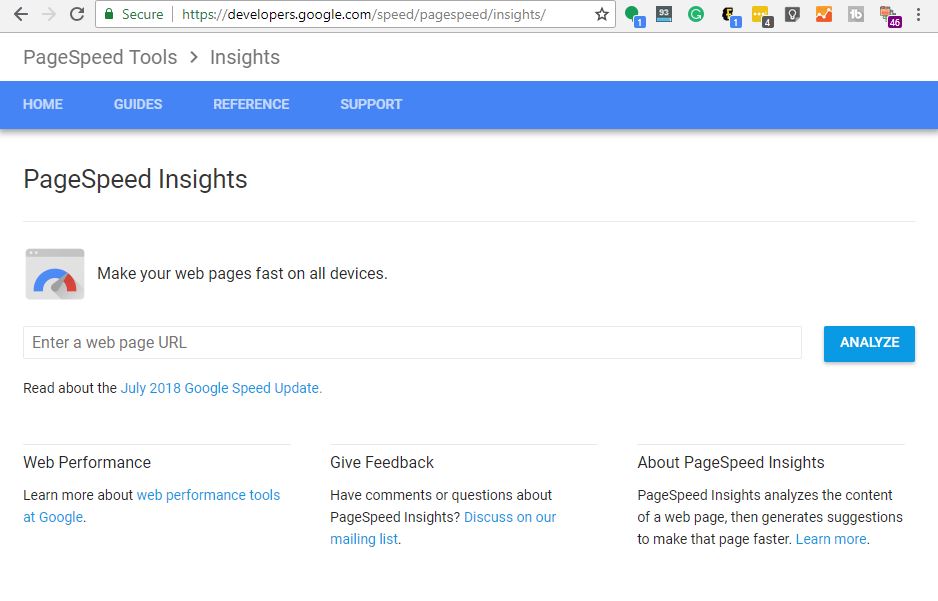
The first thing to know about this tool is that it analyzes single pages – not your entire website all at once. So, be prepared to analyze a variety of pages from your site to make sure they’re each performing the way you want them to.
To begin, you’ll enter the name of your website into the space where it says “Enter a web page URL” and then click the blue ANALYZE button. After the tool completes its analysis, your results will appear.
Here’s a peek at the results returned for cnn.com:
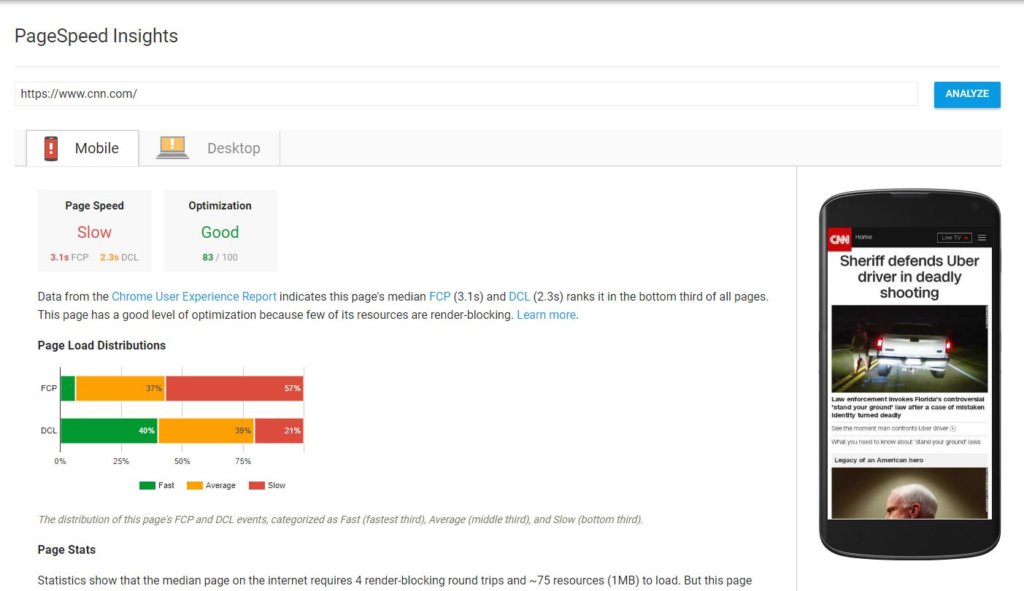
You’ll notice that there are results for both Mobile and Desktop. You’ll want to look at both sets of results for your website. But we’ll only look at CNN’s mobile results for the sake of brevity.
You can see that the page speed for CNN’s homepage was slow for mobile users at the time I ran the analysis, but that the optimization is good. Even the most well-known websites can have problems with the speed of their website.
The good thing is that the PageSpeed Insights tool doesn’t stop with a simple analysis of how speedy your site is. It also gives optimization suggestions for further improving the speed of the site along with identifying optimizations already present. (See the following image.)
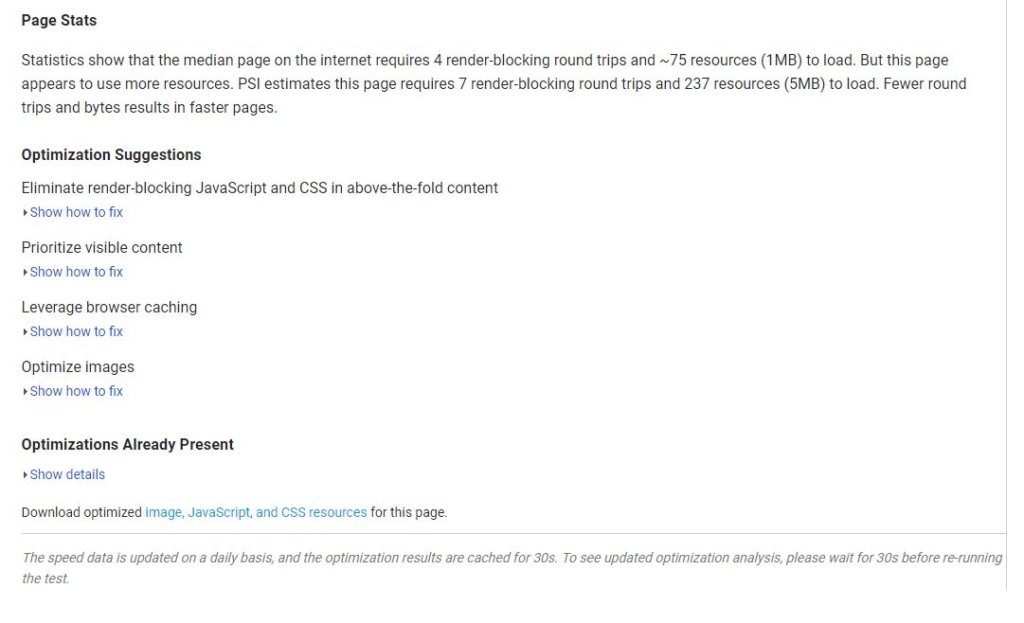
But don’t worry if you don’t understand the optimization improvements your website needs. That’s why you have a webmaster, right? Your webmaster will understand what can and can’t be done to improve the speed of your website.
You also need to make your website error-free.
Google has another free tool you can use to begin tackling the errors on your site. It’s called Google Search Console.
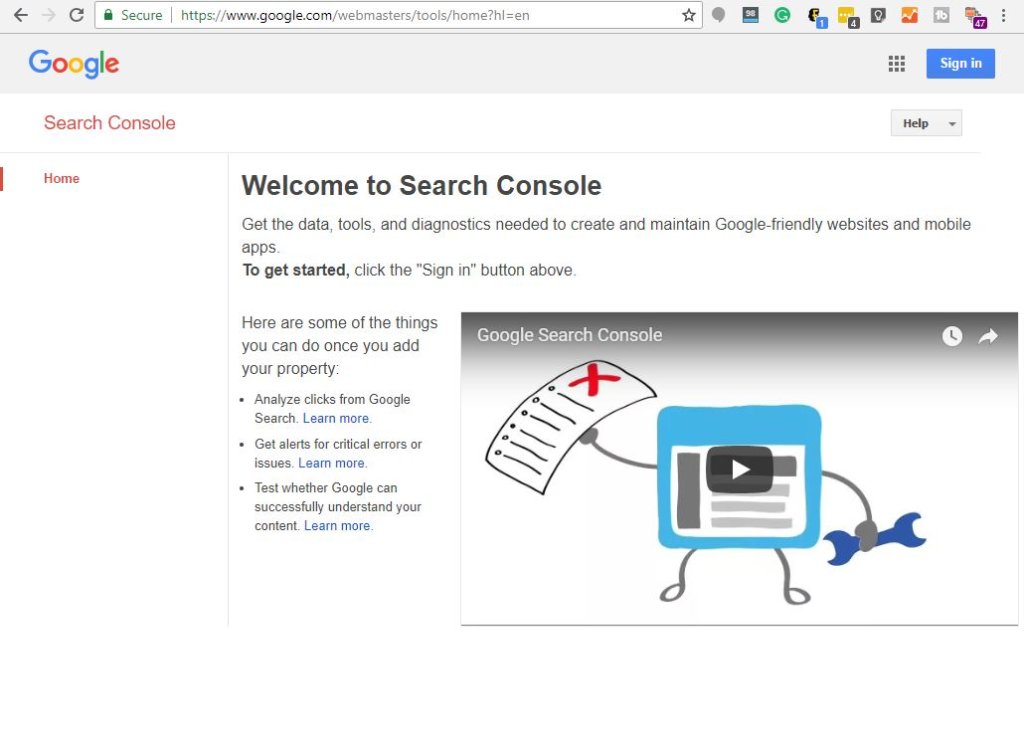
To use Search Console, you’ll need a Google account and to add some code to your website. But, if you’ve already got your website connected to Google Analytics, the code for Analytics will work to enable Search Console and you don’t have to add Search-Console-specific code to your site.
(Google Analytics is a great tool for learning more about the people who visit your site and what they do when they get there. If you don’t already have it installed on your site, I suggest you do so.)
As you can see in the image, one of the things Search Console will do for you is test whether Google can understand the content of your website. It does this by examining your sitemap. Your sitemap is a structured list that describes your website in terms a computer can understand.
You definitely want the search engines to understand what’s on your website. If the search engines can’t, then any work you put into developing SEO marketing strategies won’t matter much.
Another benefit of using Search Console is that it will identify critical errors or issues on your website. It will tell you if you have broken links or server problems. And by looking at the errors your webmaster can identify anything from minor coding errors to whether your site has been hacked.
Is your site easy to navigate?
Navigation is a key element of Google’s evaluation of website user experience. If you’ve ever spent time on a website struggling to find the information you wanted, then you know what poor navigation is like. It’s frustrating!
You want to avoid having visitors to your site feeling confused about where the information they want is. To make sure your site is easy to navigate, you’ll want to follow these tips:
- Make sure the navigation is clear and legible.
Stay away from tiny, narrow or overly stylized fonts.
- The navigation should be divided into logical categories.
This doesn’t mean that you need every category listed in your main menu – just the major ones. You can use drop-down menus for the sub-categories.
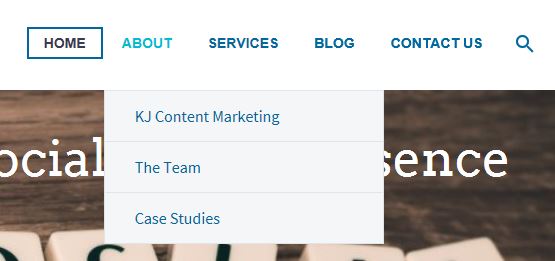
For example, you can see in the image below that the main menu is comprised of the categories Home, About, Services, Blog, and Contact Us. You can also see an example of a drop-down menu for About consisting of the categories KJ Content Marketing, The Team, and Case Studies.
- Don’t get fancy with your navigation.
We’re all creatures of habit. We’re used to having the menus on websites look a certain way. So, make your navigation feel and look familiar to the people who visit your site.
- Consider adding a search feature.
Even if you’ve done a great job of ensuring your navigation is legible, logical and familiar there still may be a few visitors who can’t quickly find what they’re looking for. That’s why you should consider adding a search function to your menu.
You probably noticed that we have one in the far right of our menu.
- Consider adding breadcrumbs.
Breadcrumbs help your website visitors know where they are on your website. They look like “Home > SEO Marketing > How To Create Successful SEO Marketing Strategies For Your Small Business”

Breadcrumbs are also clickable. So, in the example above you could go immediately to Home or SEO Marketing. And this enhances the user experience.Finally, breadcrumbs help SEO. They provide another way for the search engines to understand how your website is structured. They lower your site’s bounce rate because people know where they are when they find your site from a search and are more likely to explore other parts of your site.
- Test your site’s navigation.
Of course you need to test the navigation for functionality on both desktop and mobile platforms, but don’t stop there. Ask your employees, friends and family to help you out with testing the menus on your website. Ask them if the menus are easy to read and understand.
Is your website secure?
Web security is a big deal – not just to large websites, but to yours as well.
In July 2018, Google’s Chrome browser began marking non-HTTPS sites as ‘not secure.’
(HTTPS stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure. It’s the transfer of information to and from your website that needs to be secure.)
Think of it this way, when you visit a website and are really interested in getting a special report, signing up to get email notifications about sales, registering for a giveaway, or making a purchase you enter your email address and/or credit card information.
You don’t want your email address or credit card stolen as they transfer across the internet from your computer to the website you’re visiting. That’s what HTTPS helps prevent.
Even if you don’t ask for people’s email address, credit card or any other identifying information your website still needs to be secure. That’s because Chrome will flag it to anyone trying to access your website as being not secure and question whether they really want to proceed or if they want to go back to safety.
Yup, it really says “go back to safety.” I don’t know about you, but it always causes me to think twice about visiting a website that my browser has identified as unsafe.
The way you get an HTTPS for your website is to request an SSL certificate from your hosting provider.
However, just because your website’s URL does contain an HTTPS at the beginning which indicates it has an SSL certificate, that doesn’t mean that your site is 100% secure. You also need to make sure that each of the internal links on your site point to the HTTPS version of your site as well and not the old HTTP version.
Is your website mobile friendly?
The last of the technical checks for your website’s SEO marketing strategy is for mobile friendliness. More and more people are using their phones to access the web these days and your website needs to be ready for visitors from desktop, tablet and mobile devices.
For a website to be mobile friendly, all its information – navigation, images, text, videos, links – needs to be easily accessible on a smartphone.
Google’s Search Console can help you determine the mobile-friendliness of your site. When you open Search Console for your website, you’ll see a menu on the left. Select Search Traffic and then select Mobile Usability.
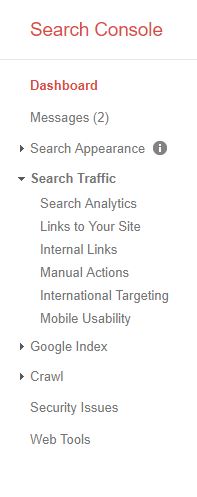
Google will then display the results for your site’s Mobile Usability. You’ll want to correct any issues found because websites with mobile usability issues may not rank as well in mobile search results. And with search traffic from mobile devices on the rise, you want to be sure your website is ready.
On-Page SEO Marketing Strategies
Each of the pages on your site needs to work together to paint a consistent picture for the search engines regarding what your website is about. For example, if you’re a plumber, you wouldn’t want to have pages on your site that focus on the best places for destination weddings.
Your Overall SEO Website Strategy
For your on-page SEO marketing strategies to work, you need to create the overall marketing strategy for your website. You start by thinking about your business and for what you want people to know you.
You might want to be known for the best cheesecake in town or as the most reliable bank in town or as the source for the best virtual assistants in the country. Getting clear about what you offer and why you’re different is the first step in finding appropriate keywords that work together for each of the pages on your site.
Although there are free tools available for finding keywords, I don’t think they give you as much detailed information as you need. I prefer to use SEMRush for all my work with helping clients develop their overall website SEO marketing strategy. The tool is pricey, but the detailed information it provides about keywords is critical to developing the foundation for your on-page SEO strategy.
Once you’ve determined the optimum keywords for each of your pages and posts, you’re ready to put those keywords to work for you.
Putting The Keywords To Work
The keywords you select for each page or post need to appear in several places:
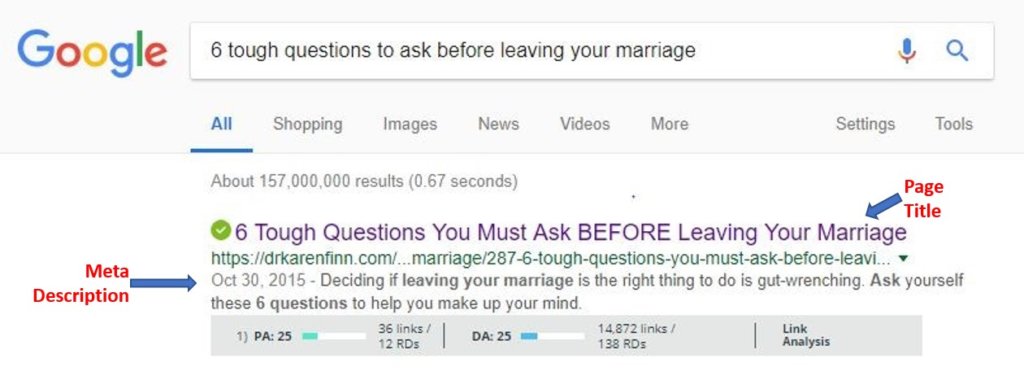
- Page title (the purple text in the image below)
- URL (the green text in the image below)
- Meta description (the gray text under the URL in the image below)
- <h1> tag
The <h1> tag is usually the title of the page or post and is the largest text on the page so that it stands out.
- <h2> tag
The <h2> tag is a subheading and is used to help the reader understand the organization of your page/post and emphasize that the page/post is about the keyword you’ve selected for it.
- First 100-150 words of the page/post and lightly sprinkled throughout the page/post
You want people who find one of the pages on your website by search to quickly know that your page/post addresses their concern. One of the quickest ways to do this is to include your keyword early in the text and to remind the reader of how you’re addressing their concern by occasionally mentioning the keyword again throughout the page/post.
- Alt tag for the main image
If someone is accessing a page on your website and they are visually impaired, the alt tag is what will be read to them in lieu of viewing the image. So you want to confirm that the post is about what the keyword promises by including it in the alt tag for the main image.
If you have a WordPress website and use the plug-in Yoast, then putting your keywords to work on each of your pages/posts is straightforward.
As an advanced technique for boosting the SEO value of other pages/posts, you can also use internal links to other pertinent and related information on your website using the keyword for that other page.
For example, I wrote a blog post defining digital content marketing and it has the keyword “what is digital content marketing.” If I can naturally use the phrase what is digital content marketing in another blog post, then I’ll add a link to the article – just like I did here.
SEO Marketing Strategy For Other Sites
Believe it or not, you can actually use other sites to boost your website’s SEO. You’re probably most familiar with the idea of sharing links to your site and/or blog posts on social media.
When someone clicks the link to your site, it signals Google that the content is interesting and that other sites are telling people about it. Google does this because people only share, cite and reference content they like. And if some people like it, then other people probably will too.
The whole premise of an SEO marketing strategy for other sites is creating backlinks to your site.
Besides people liking and sharing posts about your website on social media, there are several other types of sites to consider for creating links back to your website (aka backlinks).
- Guest posting
Guest posting is writing a post for someone else’s blog. To make this work for you, you’ll need to do some research to determine which relevant blogs accept guest posts and which of those allow backlinks. Keep in mind that some blog owners expect to be paid for guest posts, so plan what your budget is before going too far.
- Blog comments
By commenting with the intention of creating engaging conversation on blogs that are related to your business mission, you start to build credibility. By doing so consistently, you build your reputation as a thought-leader in your area of expertise.
As you become more well-known as an expert, when you occasionally add a link to something on your site that contributes to a blog post you’re commenting on, people will click your link to see what else you have to say.
- Posting in forums and/or Facebook groups
This is similar to posting blog comments, but in this case, you will probably need the permission of the forum or group owner before posting any links to your website.
- Repurposing content on relevant websites
There are all kinds of online magazines covering just about every topic under the sun. And each of these online magazines is looking for relevant and well-written content.This is the opportunity you need to submit your best posts along with the URL where each was originally published to appropriate magazines. When a magazine picks up your post, it will provide a link to the original content on your site. And this link is a backlink to your website.
Conclusion
There is a lot of information here about the three different types of SEO marketing strategies you need for your small business. However, the good news is that you don’t need to do all three of them at once.
The first step is to make sure your strategy for your website itself is fine-tuned. By doing so, Google will determine if your site can deliver good content regardless of whether people are using their smart phones, desktops or tablets to visit your site.
Once your website is ready, then it’s time to develop and implement your SEO strategy for each of the pages on your site. This is where you make sure the content on your site is what people are searching for.
And after you’re delivering great content on your site, you’re ready to start figuring out how to leverage other sites to increase the visitors to yours.
There’s a lot of work involved in creating successful SEO marketing strategies for your business. However, by proceeding in this order, each strategy builds on the one before and is more easily accomplished.
